
A. Heart and heart wall layers
1. The heart is located on the left side of the mediastinum
2. The heart consists of three layers. Cardiovascular System
- epicardium is the outermost layer of the heart.
- The myocardium is there middle layer and is the actual contracting muscle of the heart.
- the endocardium is the innermost layer and lines the inner chambers and heart valves.
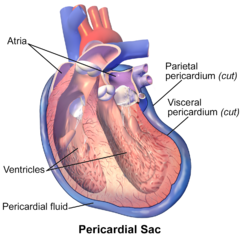
B. Pericardial sac
1. Encases and protects the heart from trauma and infections.
2. Has two layers
- The parietal pericardium is the tough, fibrous outer membrane that attaches anteriorly to the lower half of the sternum, posteriorly to the thoracic vertebrae, and inferiorly to the diaphragm. Cardiovascular System
- The visceral pericardium is the in inner layer that closely adheres to the heart
- The pericardial spase is between the parietal and visceral layers,it holds 5 to 20 ml of pericardial fluid,lubricants the pericardial surfaces,and cushions the heart.
C. There are four heart chambers
- The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the superior and inferior vena cava.
- The right ventricle receives blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the lungs via the pulmonary artery.
- The left atrium receives oxygeneted blood from the lungs via four pulmonary viens.
- The left ventricle is the largest and most muscular chamber it receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the left atrium and pumps blood into the systemic circulation via the aorta. (Cardiovascular System)
D. There are four valves in the heart
1. There are two atrioventricular valves the tricuspid and the mitral, which lie between the atria and ventricles.
- The tricuspid valve is located on the right side of the heart.
- The mitral (bicuspid)valve is located on the left side of the heart. (Cardiovascular System)
- The aterioventricular valve close at the beginning of ventricular contraction and prevent blood from flowing back into the atiria from the ventricles these valves open when the ventricle relaxes.
Tota Ram = Tricuspid Right side
Banwari Lal = Bicuspid (mitral) Left side
2. There are semilunar valves the pulmonic and the aortic.
- The pulmonic semilunar valve lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery.
- The aortic semilunar valve lies between the left ventricle and aorta.
- The semilunar valves prevent blood from flowing back into the ventricles during relaxation, they open during ventricular contraction and close when the ventricles begin to relax.
E. sinoatrial (SA) node
- The main pacemaker that initiates each heartbeat.
- It is located at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium.
- The sinoatrial node generates electrical impulses at 60 to 100 times per minute and is controlled by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
F. Atrioventricular (AV) node
- Located in the lower aspect of the atrial septum.
- Recives electrical impulses from the sinoatrial node.
- If the sinoatrial node fail, the atrioventricular node can initiate and sustain a heart rate of 40 to 60 beats/min.
G. The bundle of His
- A continuation of the AV node, located at the interventricular septum.
- It branches into the right bundle branch, which extends down the right side of the interventricular septum, and the left bundle branch, which extends into the left ventricle. (Cardiovascular System)
- The rightand left bundle branches terminate into purkinje fibers.
H. Purkinje fibers
- Purkinje fibers are a diffuse network of conducting strands located beneath the ventricular endocardium.
- These fibers spread the wave of depolarization through the ventricles.
- Purkinje fibers can act as the pacemaker with a rate between 20 to 40 beats/minute when higher pacemakers (such as the SA node) fail.
I. Coronary Arteries
- The right coronary artery blood supplies to the Cardiovascular System right atrium and ventricle the inferior position of the left ventricle, the posterir septal wall, and the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes. (Cardiovascular System)
- The left main coronary artery consists of two major branches, the left anterior descending and the circumflex arteries.
- The left anterior descending artery supplies blood to the anterior wall of the left ventricle,the anterior ventricular septum and the apex of the ventricle.
- The circumflex artery supplies blood to the left atrium and lateral and posterior surfaces of the left ventricle.
J. Heart Sounds
- The first heart sound (S1) is heart as the atrioventricular values close and is heard loudest at the apex of the heart.
- The second heart sound(S3) is heard when the semilunar valves close and is heard loudest at the base of the heart.
- A third heart sound (S3) may be hired if ventricular wall compliance is decreased and structures in the ventricular wall vibrate; this can occur in conditions such as congestive heart failure or valvular regurgitation.
- A Fourth heart sound (S4) may be heard on atrial systole if resistance to ventricular filling is present; this is an abnormal finding, and the causes include cardiac hypertrophy, disease, or injury to the ventricular wall.
K. Heart rate
- The faster the heart rate, the less time the heart has for filling, and the cardiac output decreases.
- An increase in heart rate increase oxygen consumption.
- The normal sinus heart rate is 60 to 100 Beats per minute.
- Sinus tachycardia is a rate more than 100 beats per minute.
- Sinus bradycardia is a rate less than 60 beats per minute.
L. Autonomic Nervous System
1. Stimulation of sympathetic nerve fibers release the neurotransmitter norepinephrine, producing an increased heart rate, increased conduction speed through the atrioventricular node, increased atrial and ventricular contractility, and peripheral vasoconstriction. Stimulation occurs when a decrease in pressure is detected. Cardiovascular System
2. Stimulation of the parasympathetic nerve fibers releases the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which decreases the heart rate and lessens atrial and ventricular contractility and conductivity, stimulation occurs when an increase in pressure is detected.
M. Blood pressure (BP) control
1. Baroreceptors, also called pressoreceptors, are located in the walls of the aortic arch and carotid sinuses.
2. Baroreceptors are specialized nerve endings affected by changes in arterial BP.
3. Increases in arterial pressure stimulate baroreceptors, and the heart rate and arterial pressure decrease.
4. Decreases in arterial pressure reduce stimulation of the baroreceptor sand vasoconstriction occurs, as does an increase in heart rate.
5. Stretch receptors, located in the vena cava and the right atrium respond to pressure changes that affect circulatory blood volume.
6. When the BP decreases as a result of hypovolemia, a sympathetic response occurs, causing an increased heart rate and blood vessel constriction when the BP increase as a result of hypervolemia an opposite effect occurs.
7. Antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) influences BP indirectly by regulating vascular volume.
8. Increases in blood volume result in decreased anti-diuretic hormone release, increasing diuresis, decreasing blood volume, and thus decreasing BP.
Also Read-
Cardiovascular System Related Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Pericardial Effusion Symptom Diagnosis Treatment
Blood MCQs – Question For Nursing Exam
Components of Blood and Functions
Cardiac Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Blood Transfusion – Complication – Precautions and Responsibility.
Uttarakhand govt MSc entrance exam for nursing
Dr. NTRUHS MSc Nursing Entrance Exam Paper
Thanks for reading. if you have any query please comment below. we answer your query as fast as we can.






What is cardio