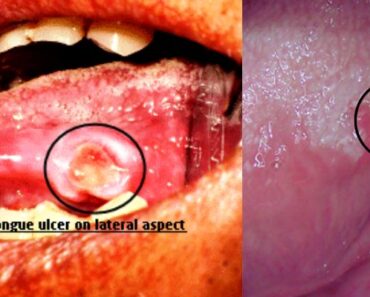
leukoplakia meaning – Leukoplakia is a condition characterized by the presence of thick, white patches or spots on the inner surface of the mouth. is a condition that should not be taken lightly. These patches can develop on the gums, tongue, cheeks, and other areas within the oral cavity. we are trying to provide a comprehensive overview of leukoplakia, including its types, symptoms, and easily available treatment options.

The exact cause of leukoplakia is unknown, but it has been strongly linked to certain lifestyle factors. it has been linked to the use of tobacco, smoking, and alcohol consumption.
Types of Leukoplakia
There are two main types of leukoplakia: homogenous and nonhomogenous.
- Homogenous Leukoplakia: This type of leukoplakia is characterized by uniformly white plaques on the oral mucosa. Homogenous leukoplakia typically carries a lower risk of malignant transformation into oral cancer.
- Nonhomogenous Leukoplakia: Nonhomogenous leukoplakia presents as mixed red and white nonuniform patches in the mouth. This type of leukoplakia carries a higher risk of malignant transformation into oral cancer.
Causes of Leukoplakia
The exact cause of leukoplakia is unknown, but it has been strongly linked to certain lifestyle factors. Individuals who regularly engage in habits such as chewing tobacco, smoking, and consuming alcohol are at a higher risk of developing leukoplakia. It is important to note that not everyone who indulges in these habits will develop leukoplakia, but the risk is significantly increased.
Leukoplakia Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of leukoplakia is crucial for early detection and intervention. The following symptoms may indicate the presence of leukoplakia:
- White, red, or dark patches in the mouth.
- Ear pain experienced during swallowing.
- Difficulty in opening the jaw.
- Patches that persist for more than two weeks without healing.
Treatment of Leukoplakia
When it comes to diagnosing and treating leukoplakia, the primary goal is to eliminate these patches that lead to oral cancer. Prompt treatment is essential to stop its progression. The first step in treatment is to address the underlying cause. Encouraging individuals to stop using tobacco and alcohol, as these substances are important contributors to the development of leukoplakia. Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol intake increase the chances of a cure. Here are some common treatment options:
- Lifestyle Changes: Ceasing the use of tobacco and alcohol is crucial in managing leukoplakia. These substances contribute to the development and progression of the condition.
- Oral Vitamin A and Beta-Carotene Supplements: These supplements can use in the treatment of leukoplakia by promoting the healing of white patches in the mouth.
- Surgical Removal: In cases where the leukoplakia patches do not respond to conservative management, surgical removal may be necessary. This procedure aims to eliminate the affected tissue and reduce the risk of malignant transformation.
- Dietary Modifications: Consuming a diet rich in fruits and vegetables can support overall oral health and assist in the management of leukoplakia.
- Photodynamic Therapy: This innovative treatment approach utilizes light-activated cancer drugs to target and destroy leukoplakia cells.
- Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy involves freezing the leukoplakia patches, leading to their removal. This technique can be an effective treatment option for certain cases.
- Cauterization: Cauterization involves using an electrically heated needle to remove the leukoplakia patches. This procedure aims to eliminate the affected tissue and promote healing.
Complications
If left untreated, leukoplakia can lead to several complications, including:
Permanent Tissue Damage: The persistent presence of leukoplakia can result in permanent damage to the oral tissues, affecting their functionality.
Increased Risk of Oral Cancer: Approximately 3 to 17% of individuals with leukoplakia develop squamous cell carcinoma, a common type of oral cancer. Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial to minimize this risk.
Conclusion
Leukoplakia, characterized by white patches in the mouth, is a condition that demands attention. It is essential to be aware of the types, symptoms, and available treatment options to ensure early detection and management. By making lifestyle changes, seeking appropriate medical interventions, and maintaining regular dental check-ups, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with leukoplakia and promote optimal oral health.
Read more-
The mouth structure function and Diseases
Canker sores type causes symptoms & treatment
Anatomy and Physiology of the Urinary System
Nursing model question paper for JIPMER AIIMS DSSSB