The bleeding after a fixed interval from the uterus is called menstruation. Menses also are known as a period, monthly or menstrual cycle. The menstruation cycle involves the monthly release of an egg (ovum). The process called ovulation, it prepares for the possibility of pregnancy each month. With bleeding due to the shedding of the uterine lining at the end of the cycle. The first menstrual cycle, or first menstrual bleeding, in female known as Menarche.
The onset of the Menstrual cycle is considered from the first day of bleeding. The days between two menstrual periods are counted from the beginning of the first to the beginning of the second. Typically, in young women and adult women it is 21 to 45 days in length, the time is 21 to 31 days (28 days on average). Bleeding lasts on average 20 to 80 ml and lasts 2 to 7 days. Women start their menstruation from puberty, which usually occurs at the age of 9 to 16 years. And this menstruation lasts throughout the life of women until menopause occurs which is in the age of 40 to 60 years. The control of menstruation is done by the anterior pituitary, which secretes the key hormones FSH and LH to control it.
Menstruation or Menstrual cycle described in four phases:
- Proliferative Phase
- Secretory Phase
- Premenstrual Phase
- Menstrual Phase
Proliferative Phase or Follicular Phase : (6 to 14 Days)
- The Proliferative Phase is to say in other words as follicular phase.
- Length of this phase is highly variable. This phase typically takes place from 6 to 14 days.
- This is the time from the end of the menstrual phase to the ovulation.
- At the beginning of this phase, the group of approximately 20 secondary follicles begins to grow in both the ovaries with the effect of FSH and start the secretion of estrogens and inhibin.
- Approximately 6th day, a secondary follicle of one ovary become dominant follicle by growing more than the other. Due to this, the growth of all follicles other than the Dominant Follicle is stopped and they become atresia.
- The remaining left Dominant follicle becomes a mature (Graafian) follicle.
- The Graafian follicle becomes enlarge continuously for more than 20mm diameter being prepared for ovulation, which occurs on LH at approximately 14 days.
- In this stage, there is multiplication in endometrial cells and the endometrium becomes thick.
- Due to the formation of new stratum functionalis from mitosis in stratum basalis, the thickness of endometrium becomes almost double (4-10 mm).
- Rising levels of estrogen are responsible for triggering a surge of LH approximately mid-cycle. This LH surge triggers ovulation, marking the end of the proliferative phase.
Secretory Phase, Luteal Phase or Post Ovulatory Phase (14 to 24 Days)
- The secretory phase is the time between ovulation and the next menses starting.
- The time of this phase is approximately fixed (14 days).
After the ovulation with the effect of FSH & LH, the remaining Graafian follicle corpus gets converted into luteum, which excretes progesterone estrogen relaxin and inhibin. - Under the influence of progesterone, the endometrium becomes oedematous(enlarged blood vessels and glands).
- The secretory glands produce excessive amounts of watery mucus.
- This assists the passage of the spermatozoa through the uterus to the uterine tubes where the ovum is usually fertilized.
Premenstrual Phase (25 to 28 days)
After ovulation, the combination of progesterone, estrogen, and inhibin from the corpus luteum suppresses the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary, so FSH and LH levels decrease.
Menstrual Phase (1 to 5 days)
- At this stage, decreasing the level of the hormone starts the endometrium shading. It starts bleeding.
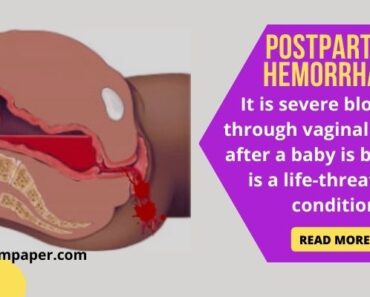
- There is a loss of 50 to 150 ml of blood in a menstrual cycle.
- At this stage, the endometrium becomes extremely thin around 2 – 5 mm. Because there is only left stratum basalis.
Abnormality of Menstrual Cycle, Menstruation & Menses – Phase :
Amenorrhea :
The medical term is the absence of menstrual period (bleeding) in a woman of reproductive age is known as amenorrhea or menostasis. There are two types of amenorrhea Primary & Secondary amenorrhea.
Primary amenorrhea – in the presence of normal growth and secondary sexual characteristics the young woman has not had her first period by the age of 16.
Secondary amenorrhea -This is when a woman who has had regular periods stops having her period for a minimum of 90 days or three months or longer. caused by Pregnancy, Breastfeeding, Menopause, Some birth control methods, Hormonal imbalance, Poor nutrition, Depression and Certain prescription drugs, etc.
Cryptomenorrhea :
Cryptomenorrhea or cryptomenorrhoea is one of the most serious conditions also known as hematocolpos. An abnormal condition in which the products of menstruation are retained within the vagina because of an imperforate hymen. Menstruation occurs but does not appear due to opposition to the outflow tract. Cryptomenorrhea may look like they are amenorrhea. Amenorrhea and Cryptomenorrhea involve no visible menstrual fluid. In the cryptomenorrhea, you will likely experience cyclical menstrual pain like cramping, Premenstrual Syndrome and tender breasts, etc. In amenorrhea, there is no menstruation for some reason.
Dysmenorrhea :
Dysmenorrhea is the medical term for painful menstruation. also known as painful periods or menstrual cramps and difficult monthly flow. mostly women’s to have mild abdominal cramps on the time that menstruation begins (first or second day of their period), and some women experience severe pain. There are two types of dysmenorrhea primary and secondary.
Primary dysmenorrhea is a common menstrual cramp that is recurrent and not a symptom of an underlying gynecologic disorder but it is related to the normal process of menstruation.
Secondary dysmenorrhea is related to some kind of gynecologic disorder. like endometriosis, adenomyosis, uterine fibroids, or infection.
Hematometra :
Hematometra or hemometra is a condition involving the collection or retention of blood in the uterus. It is a rare condition that is most commonly associated with congenital anomalies (imperforate hymen or a transverse vaginal septum) or prior surgical procedures causing obstruction of the genitourinary outflow tract. the hemometra typically presents as cyclic, cramping pain in the midline of the pelvis or lower abdomen and back pain. the unusual case of hematometra in a healthy and active adolescent female with no prior risk factors.
Hematosalpinx :
Hematosalpinx (hemosalpinx) is a medical condition involving bleeding into the fallopian tubes. most commonly in tubal pregnancy also be associated with endometriosis or tubal carcinoma. Symptoms are pelvic pain and uterine bleeding.
Hypomenorrhea :
Hypomenorrhea or hypomenorrhoea is the scientific term for chronically light periods menstrual blood flow. It is the opposite of menorrhagia. Everywomen’s have a little different in their menstrual cycle. The normal menstrual cycle is around three to seven days long and 30 to 80 ml bleeding average. If the female noticed that his cycle is lasting less than two days or is lighter than 30ml. This happens for a few cycles, then she has hypomenorrhea.
Menorrhagia :
Menorrhagia is heavy or prolonged vaginal bleeding with the menstrual cycle. Heavy periods caused by hormonal imbalance, IUD use, or side effects of any medicine and can be caused by an endometrial polyp, fibroids, and endometriosis.
Metrorrhagia :
Metrorrhagia is known as intermenstrual bleeding or is uterine bleeding particularly between the menstrual periods. metrorrhagia caused by an underlying disorder such as uterine fibroids, benign and malignant conditions, and hormonal imbalance.
Oligomenorrhea :
Oligomenorrhea means infrequent menstruation or very light menstruation. It is menstrual periods occurring at intervals of more than 35 days. In this condition, the woman has 4 to 9 periods in a year. Oligomenorrhea can be treated through hormonal therapy.
Polymenorrhea:
Polymenorrhea or short menstrual cycle also a form of abnormal uterine bleeding. In this condition, the menstrual cycle occurring at intervals of less than 21 days. A normal menstrual cycle for an adult woman is 24 days to 37 days long.
What are the 4 stages of menstrual cycle?
Menstruation or Menstrual cycle described in four phases
Proliferative Phase or Follicular Phase (6 to 14 Days) Secretory Phase, Luteal Phase or Post Ovulatory Phase (14 to 24 Days) Premenstrual Phase (25 to 28 days) Menstrual Phase (1 to 5 days)
Which age periods will stop?
After Menarche This menstruation lasts throughout the life of women until menopause occurs which is in the age of 40 to 60 years.
How many days is a normal period last?
Typically, in young women and adult women it is 21 to 45 days in length, the time is 21 to 31 days (28 days on average).
What happens in menstrual cycle?
The bleeding after a fixed interval from the uterus is called menstruation. Menses also are known as a period, monthly or menstrual cycle. The menstruation cycle involves the monthly release of an egg (ovum).
Thanks.