A head injury is any trauma to the skull, skull, or brain. The injury may be only a minor bump on the skull or a serious brain injury. Mild traumatic brain injuries usually require no treatment other than rest and over-the-counter pain relief to treat headaches. But sometimes the injury is very serious and may require ICU care and even (Craniotomy) surgical treatment.
During any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. treat the patient to prevent increase ICP by positioning, by medications like mannitol diuretics and corticosteroids.
Surgical treatment Craniotomy is often used for patients of Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI). In closed head injury, Craniotomy surgery does not correct the problem. But the overall goal of all surgical treatment is to prevent secondary injury. by helping to maintain blood flow and oxygen in the brain and minimize swelling and Intracranial pressure.
Medical Treatment of increased intracranial pressure –
- Positioning the patient in an upright position with the head of the bed at 30 degrees will lower ICP by increasing venous drainage from the cranial cavity.
- Hyperventilation: Hyperventilation is the most rapid and effective means of lowering ICP, the lowering of the PaCC02 leads to constriction of the cerebral blood vessels. reducing CBF & thereby deducing the ICP But the effects are short-lived because the body quickly compensates. The PaCO should be maintained between 25-33 mm Hg
- Mannitol- Mannitol acts to reduce the ICP by plasma expansion & osmotic effect There is an immediate plasma expansion effect that reduces the hematocrit and blood viscosity, thereby increasing CBF. osmotic gradient helps to move the fluid from the tissue to the blood vessels. Dosage is 0.5-1 gm/kg (37.5-50 gm) IV q6h; keep osmolarity <315; do not give for more than 48h
- Loop diuretics: Drugs that increase urine output to reduce excessive fluid in the system may be used to treat high intracranial pressures by reducing blood volume & tissue volume in the brain. This agent causes a reduction in the CSF. It helps to prevent disequilibrium syndrome.
- Corticosteroids- Corticosteroids are best used to treat increased ICP in the setting of vasogenic edema caused by brain tumors or abscesses; they act by their stabilizing effect on the cell membrane and by inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandins, however, these agents have little value in the setting of stroke or head trauma. Dosage is dexamethasone (Decadron) 10 mg IV or IM, followed by 4-6 mg IV, IM or PO q6h.
Craniotomy Surgery:
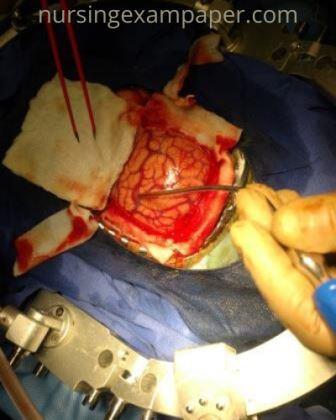
A craniotomy is a surgical procedure that involves an incision through the cranium to the removal part of the bone from the skull to expose the brain. Specialized tools are used to remove the section of bone called the bone flap. The bone flap is temporarily removed, then replaced after the brain surgery has been done.
Types of Craniotomy
- Extended Bifrontal Craniotomy
- Minimally Invasive Supra-Orbital “Eyebrow” Craniotomy
- Retro-Sigmoid “Keyhole” Craniotomy
- Orbitozygomatic Craniotomy
- Translabyrinthine Craniotomy
Preoperative interventions –
Ensure that informed consent has been obtained Prepare to shave the client’s head as prescribed (usually done In the operating room) and cover the head with an appropriate cover.ng Stabilize the client before surgery.
Postoperative interventions-
- Monitor vital signs and neurological status every 30 to 60 minutes.
- Monitor for increased intracranial pressure. Monitor for a decreased level of consciousness, motor weakness or paralysis, aphasia, visual changes, and personality changes. Maintain mechanical ventilation and slight hyperventilation for the first 24 to 48 hours as prescribed to prevent increased intracranial pressure.
- Assess the physician’s prescription regarding client positioning.
- Avoid extreme hip or neck flexion, and maintain the head in a midline neutral position.
- Provide a quiet environment.
- Monitor the head dressing frequently for signs of drainage after Craniotomy.
- Mark any area of drainage at least once each nursing shift for baseline comparison Monitor the Hemovac or Jackson-Pratt drain, which may be in place for 24 hours. Maintain suction on the Hcmovac or Jackson-Pratt drain.
- Measure drainage from the Hemovac or Jackson-Pratt dram every 8 hours, and record the amount and color.
- Notify the physician if drainage is more than the normal amount of 30 to 50 mL per shift. Notify the physician immediately of excessive amounts of drainage or a saturated head dressing. Record strict measurements of hourly intake and output. Maintain fluid restriction at 1500 mL/day as prescribed.
- Monitor electrolyte levels. Monitor for dysrhythmias, which may occur as a result of fluid or electrolyte imbalance.
- Apply ice packs or cool compresses as prescribed; expect periorbital edema and ecchymosis of one or both eyes, which is not an unusual occurrence.
- Provide range-of-motion exercises every 8 hours. Place anti-embolism stockings on the client as prescribed. Administer anticonvulsants, antacids, corticosteroids, and antibiotics Administer analgesics such as codeine sulfate or acetaminophen (Tylenol) as prescribed for pain.
Complications:- Include Increased ICP from cerebral edema, hemorrhage, or obstruct, one of the normal flow of CSF. hematomas, hypovolemic shock, hydrocephalus, respiratory and neurogenic complications, pulmonary edema, and wound infections. Fluid and electrolyte imbalances include diabetes insipidus and inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone.
Rehabilitation
Most people who have had a significant brain injury will require rehabilitation. They may need to relearn basic skills, such as walking or talking. The goal is to improve their abilities to perform daily activities.
Therapy usually begins in the hospital and continues at an inpatient rehabilitation unit, a residential treatment facility or outpatient services. The type and duration of rehabilitation are different for everyone, depending on the severity of the brain injury and what part of the brain was injured.