In this article, we are providing the details of some of the tools used in Gynecology and Obstetrics procedures which will help you to clear the upcoming Nursing Exams. that Instruments Used in Gynecology and Obstetrics are used by a maximum gynecologist to treat patients. Surgical instrument pictures and their names
Obstetrics instruments with names
Cusco’s Bi-valved Speculum –
- Self-retaining bi-valved speculum
- Cervical and vaginal inspection
- Used for pap smear, cervical Bx, Colposcopy
- Handles slightly concave to collect drained blood and secretion

Fergussons Tubular Vaginal Speculum –
The vaginal speculum helps diagnose and treat vaginal and uterine disorders. This type of vaginal speculum was devised by surgeon Sir William Fergusson (1808-77)

Auvard’s Weighted self-retaining speculum –
The wide Jaw of Auvard’s Weighted Self-Retaining Speculum for Better Visualization Detachable to provide self-retaining property Smooth edges to prevent soft tissue damage. The blade is slightly concave and has two holes on each side for fixing the tool with the buttocks. This speculum handle has a channel for blood and other vaginal discharge to escape. The device has a self-retaining property due to the weight attached to its handle.
It was used to retract the posterior vaginal wall in operations on the anterior vaginal wall, cervix, and uterine procedures. For example vesicovaginal fistula repair, anterior colporrhaphy, vaginal hysterectomy, etc.

Soonawala’s self-retaining Vaginal speculum –
It is a Z-shaped instrument that is made of stainless steel. It has two blades in opposite directions from the handle, one is shorter (6 cm long, wide and rectangular in shape) and the other is longer (11.5 cm long narrow, and with a rounded end). it is made self-retaining by the weight attached to the handle.
Soonawala’s speculum is used the short blade to retract the posterior vaginal wall and expose the cervix before opening the pouch of Douglas. after the opening pouch of Douglas inserted a long blade. the speculum was specially designed for vaginal sterilization.

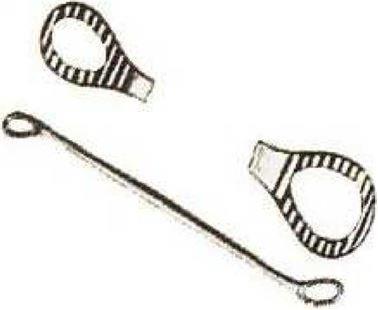
Sim’s Anterior Vaginal wall retractor –
It is a long narrow, metal instrument with oval fenestrated ends. Two serrated ovals are set at an angle to the shaft. This instrument is introduced with the angle at the oval facing upwards.
It is used along with sims speculum to retract anterior vaginal wall so its uses are the same as those for sims speculum. it is also used as a blunt curette. while D&C/E removes retained products after second-trimester abortion or retained placental bits after delivery.
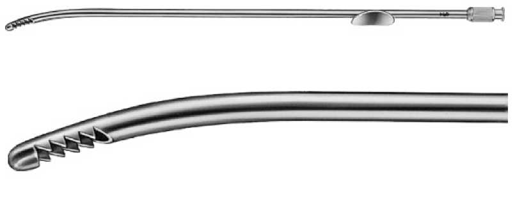
Blake’s Uterine Curette –
Blake Uterine Curette is a specialized instrument commonly used in gynecological surgeries. it has two ends (sharp and blunt) and some have a single end with a handle. The blunt end is used to remove conception products from the uterine cavity for therapeutic needs. The sharp end is used to remove endometrial tissue for diagnostic purposes.

Endometrial Biopsy Curette –
It is a slender tubular blunt-ended instrument made up of stainless steel. two main types are available simple and suction biopsy curette which is open at the proximal end and has stylet. endometrial biopsy curette is slightly curved at the tip, with one or more notches with a cutting edge near the tip. and handle grip at the proximal end.
this curette is used in OPD for taking endometrial biopsy as an outpatient procedure. cervical dilatation and anesthesia are not required.
Leech Wilkonson’s Cannula –
It is a straight metal cannula, 28 cm long with a fixed conical collar at the tip with spiral grooves over it and there is Luer lock mount at the other end. This cannula is better suited for multiparous patients with the patulous cervix. It is commonly used for chromo pertubation (a medical procedure where a blue dye solution is injected into the fallopian tubes) and HSG.

Hegar Dilator –
Hegar,s dilator is a slightly curved solid metallic instrument. there is a number on the instrument that indicates the maximum external diameter of the tip in mm. the hegar dilator is available in a set of 12 from 1mm to 24 mm.
it’s used in gynecological operations to dilatation of the cervix and internal os.

Hawkin Ambler dilator – Surgical instrument pictures and their names
it’s mainly used in obstetric operations for cervical dilatation. it is a single-ended 17.5 cm long curved instrument and gradually tapering near the tip. there is a circular handle at the non dilating end with a number marking on it. each dilator has a difference of 3mm from the tip to the maximum dilating portion. they are available in a set of 16pc Sizes 3-6mm – 18-21mm.

Purandare’s dilator –
It is also a cervical dilator with a guard and a long tapering end. Use of guards to prevent insertion exceeding that length and to protect against perforation. It consists of a number that represents the diameter in mm from the tip to the guard.

Uterine Sound –
it is a 12 inches (30 cm) long metallic instrument with a violin-shaped handle. and its boll tip prevents injury to the uterus. the tip is marked by inches and cm indicating the distance from the tip. angulated at a 2.5-inch distance from the tip (2.5″ normal uterocervical length).
in gynecology instrument, it is a dictum “before intrauterine procedures sounding is must”
contraindicated in suspected pregnancy, local infection, i.e. cervicitis.

Bladder Sound – Gentle curve with no markings on it Used to define an extension of bladder cystocele and vaginal hysterectomy

Green Armytage Forceps –
• Triangular tips with transverse serrations
• To hold the cut edge of the lower segment after delivery of the fetus
• Atraumatic and hemostatic
• Used in place of sponge holding forceps in for tracing cervical ears

Haywood Smith’s Ovum Forceps –
•Spoon shaped ends
•No lock, so no crushing action (Instruments Used in Gynecology and Obstetrics)
Uses – •1st trimester MTP: removalof POC aftercervical dilatation
•2nd trimester MTP: removal of retained bits of placenta
• Removal of pedunculated polyps

Vulsellum – Hold the anterior lip of the cervix.

Cervical Punch Biopsy – To Take Punch Biopsy of Cervix

Busch’s Episiotomy Scissors –
•Length 16 cm Sterilized by glutaraldehyde (Cidex)
•Shape allows easy introduction into the vagina and prevents erratic cutting
•Angle prevents butting of the instrument against the patient’s buttocks

Umbilical Scissors/ Cord-cutting scissors – 10.5 cm Blades are so curved such that on closing they meet at the tip which prevents the cord from slipping during cutting

Obstetric Forceps –
Obstetric forceps were invented by doctors of the Chamberlen family in England during the 17th century. That forceps are so many types invented till now. But only short forceps are used at present. All forceps have 2 metal branches called blades articulated by a lock.
• Left – Outlet Forceps ( Wrigley’s Outlet Forceps)
• Middle – Low or Midcavity Forceps
• Right- Rotational Forceps (Kielland forceps)

Wrigley’s Outlet Forceps –
It is a simple and delicate instrument invented by Wrigley in 1935. it is a type of short forceps with a total length of 27.5 cm. it is meant to apply on the head low in the pelvis under minimum anesthesia.
As it is not possible to exert strong traction with it, there are fewer chances of injury to the mother or fetus.

Mid cavity Forceps –

Ventouse Cup –
A ventouse (vacuum cup) is attached to the baby’s head by suction. Soft or hard plastic or metal cup is attached by a tube to a suction device. The cup fits firmly onto your baby’s head. During a contraction and with the help of your pushing, the obstetrician or midwife gently pulls to help deliver your baby.

Obstetrics and gynaecology instruments
Obstetric Hook with Crochet –
• Hook is used to applying groin traction in the dead fetus
• Hook is also used to pull down the leg of a dead fetus in transverse lie
• Crochet is used to apply traction on the fetal lower jaw, orbit, foramen magnum, etc to extract decapitated head.
• Crochet is also used to apply traction on the fetal head after craniotomy

Simpson Perforator –
• 28.5 cm long Blades with triangular tips and outer cutting edge. Blades are locked with a locking system
• Flat spring is present between the handles for bringing the blades back into their original place
• Used for Craniotomy and fetal evisceration of thorax/abdomen.

Oldham’s Perforator –
This perforating instrument was used to facilitate the removal of the fetus after an obstructed labor. The sharp point would pierce the fetal skull and closure of the handle would macerate the skull bones which when eventually removed would allow passage of the rest of the body. (Skeletal system part and functions)

Cranioclast –
First invented by Dr. James Simpson in the mid-19th century and later designed by others, cranioclast was used to destroy and remove embryos. The Instruments Used in Gynecology and Obstetrics.

Willet’s Scalp Traction Forceps –
It’s also known as Willett-Martel Scalp Flap Forceps, In 1925 Willett introduced a simple and effective method of producing pressure on the placenta by fixing toothed forceps to the scalp of the child and clamp tissue in the uterus.

Copper T (Cu 380 A) –

Heaney’s Hysterectomy Clamp –
• Ridge on one blade and a notch on the other
• No teeth the curve is facing the structure to be removed so that the ligature can be passed around the clamp

Uterine Polyp Forceps – Surgical instrument pictures and their names
Laufe Polyp Forceps are ratcheted, finger ring forceps commonly used to remove polyps from the uterus. Fenestrated, serrated, oval tips provide an ideal grasping surface for successful removal of these growths. The jaws are curved slightly to provide the user with a view unobstructed by the instrument.

Dartigues Uterus Holding Forceps –
Dartigues Uterine Elevating Forceps are designed to remove tissue, tumors, or polyps from the uterus by elevating the vaginal wall. The clamps at the ends of the ring handle curve inward toward the handles. The clamps feature smooth jaws to firmly grasp the tissue to be removed.

Ayre’s Spatula –
It is a wooden spatula that was introduced by Ayre in 1946. it is about 20 cm long. used to take Pap smear sample by scrape method. its rough surface maximum number of cells are scraped.

Langenbeck, Right Angled Retractor –
Langenbeck Retractor is a very popular surgical device that allows surgeons to pull back soft tissues and incision or wound edges during a wide range of general surgeries.

Karman’s Syringe – Used for menstrual regulation and endometrial

Karman’s Cannula –
Commonly used for endometrial biopsy and suction extraction of incomplete or missed abortion operations.

Veress Needle –
Used for creating a pneumoperitoneum.

Rubin’s Cannula –
A Rubin’s cannula was placed in the cervix. for Rubin’s test, it is diagnostic method for determining whether the fallopian tubes in the human female are occluded.

Shirodkars Cerclage Needle- Putting stitch around the cervix.

IUCD Removing Hook –

Doyen’s Myoma Screw –
The Doyen Myoma Screw is a gynecological instrument that is used to extract fibroids from the endometrium during myomectomy. The instrument is a coiled spring-like structure that is attached to a handle with an overall length of 17 cm. It is also available in 14 cm to service different anatomical requirements.

Bonney’s Myomectomy Clamp –
The instrument was designed by Great Victor Bonney of England. it is a long metallic clamp with slightly diverging blades which are set at an angle with the handles. handles have two pairs of finger bows but only the proximal pair is provided with catches.
It is used to control hemorrhage during myomectomy operation. it may be used for the same purpose in metroplasty operation also.
functions – Uterine vessels are clamped so hemostasis is maintained during operation.
The uterus is held, so it can be manipulated as necessary during the operation.
Inclusion of the round ligaments keeps the uterus anteverted and prevents downward slipping of the instrument.

Pinard’s Fetal Stethoscope –
The Pinard Horn is a type of stethoscope used during pregnancy to listen to the fetal heart rate. It is a hollow horn, often made of wood or metal, about 8 inches (200 mm) long. It acts like a trumpet to amplify the sound.
During pregnancy, listen to the baby’s heartbeat at each antenatal visit from the patient’s 16 weeks gestation, using a Pinard stethoscope.
The midwife will place the wide-open end of the Pinard on the abdomen. Keep your ear on the flatter end of the Pinard. This allows the midwife to hear and count the baby’s heartbeat.








Find gynecology & obstetrical instruments to help you provide the safest, most comfortable care possible. Whether you’re looking for a simple uterine sound or one of our advanced ultrasounds, our products are designed to do their jobs better than anyone else’s.
Great pߋst. I was checking constantly on this blog and I am impressed!
Very helpful information specifically the lаѕt part 🙂 I
care for such info a lot. I was seeking this certain info for a very long time.
Thank you and good luck.