The study of the endocrine system and its disorders is known as endocrinology. The human endocrine system is a complex network messenger system of glands and organs. It uses hormones to control and coordinate the targeted organs and their functions. it controls the body’s metabolism, energy level, response to injury, stress, reproduction, growth, and development, and regulates many other works. the endocrine system consists both of exocrine and endocrine glands. Which is given below.
Endocrine System Glands
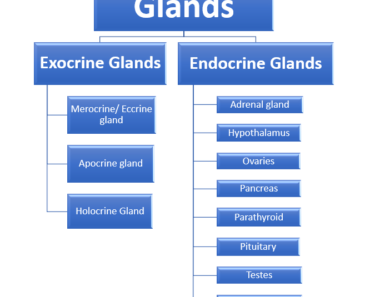
Glands are clusters of glandular epithelial cells. The glands secrete their products continuously. Which leaves through the ducts on the surface of hollow organs. This type of gland which secretes its product from epithelial cells through ducts is called the exocrine gland. Other glands that release their secretions directly into the blood and lymph are called endocrine glands.
So there are two types of glands.

1. Human Exocrine glands –
These are duct glands, as they are secreted by their secretions either directly or through a duct. Their secretions are called enzymes viz. Mucus, saliva, digestive juices, and earwax.
Three types of exocrine glands.
A. Merocrine/ Eccrine gland –
Exocrine glands secrete their secretions without damaging the cells. their secretions via exocytosis.
eg.- Sweat gland, Salivary gland, & Pancreatic glands.
B. Apocrine gland –
Some part of the cell (The apical part) comes out with its secretion. eg. –
Modified sweat glands. & Mammary Glands.
These glands are activated during puberty.
C. Holocrine Gland –
The whole part of the cell (cytoplasm) comes out with its secretion.
eg. – Sebaceous glands, meibomian glands of eyelids.
2. Human Endocrine glands –
The glands which secrete their secretion directly into the blood and lymph are called endocrine glands. These are also known as ductless glands. Their secretion is called hormones.
List of human Endocrine glands –
- Adrenal gland
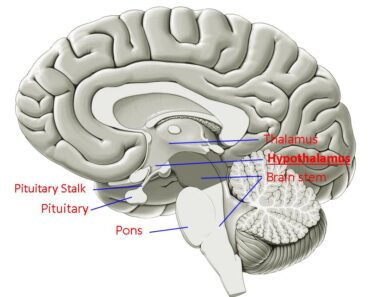
- Hypothalamus
- Ovaries
- Pancreas
- Parathyroid
- Pituitary
- Testes
- Thyroid
Largest gland of the human body – The Liver (approx 1.5 kg and around 2% of total body weight).
The largest endocrine gland of the human body is – Thyroid gland (25gm).
The smallest endocrine gland of the human body is – The pineal gland.
Hormones
Hormones are secretions of the endocrine gland, which are chemical messengers that deliver stimulatory or inhibitory signals to target cells as a result of a feedback mechanism. One time secreted hormone remains 4-6 hours in the body.
Types of Hormones On the basics of chemical nature.
According to the chemical nature, There are three types of hormones human endocrine system.
- Protein hormone/ Peptide hormones.
- Steroid hormone
- Tyrosine hormone
a. Protein hormone/ Peptide hormones.
- Derived from protein eg.- ‘P’ Gland hormones
- Pituitary gland hormones
- Pineal gland hormones
- Para thyroid gland hormones
- Pancreatic hormones
- Placental hormones (HCG, HPL) Except estrogen and progesterone
- Calcitonin (secreted by parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland also called C-cells)
b. Steroid hormones
Derived from lipids/ cholesterol eg.-
- Adrenal cortex hormones
- Glucocorticoids
- Mineralocorticoids
- sex hormones (estrogen, progesteron, testosteron)
c. Tyrosine hormone
Derived from tyrosine amino acids. eg-
- Thyroid hormones
- Tri-iodothyronine (T3)
- Thyroxine (T4)
- Calcitonin is a protein hormone
- Adrenal medullary hormones
- Epinephrine
- Norepinephrine
Types of Hormones based on the mechanism of action
According to the mechanism of action, There are two types of hormones in the human endocrine system.
a. Group – I hormones
Group- I hormones are lipophilic. mostly they are steroid hormones. these hormones act through intracellular receptors. eg.-
- Glucocorticoids
- Mineralocorticoids
- Estrogen, Androgens.
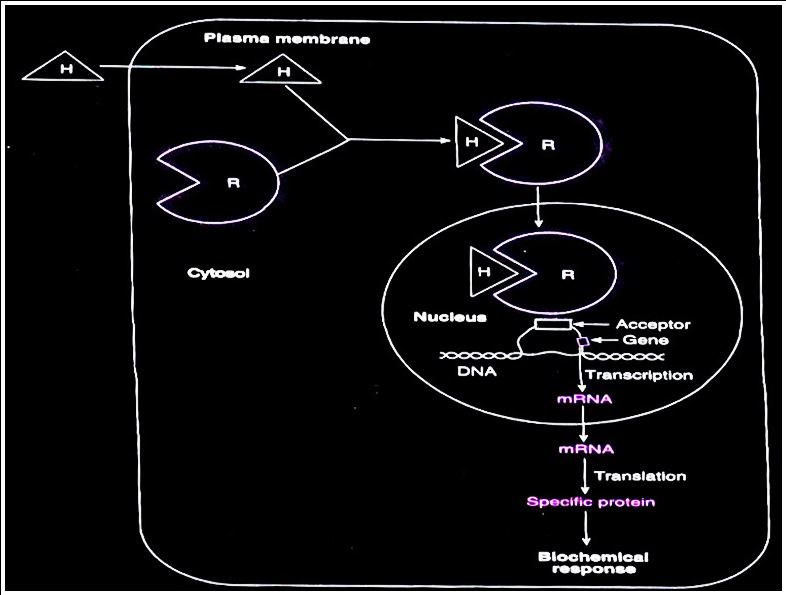
Mechanism of action
- These hormones are lipophilic so they can easily pass across the plasma membrane.
- Act through intracellular receptors located either in the cytosol or the nucleus and form receptor hormone – hormone complex / Hormone receptor complex (HRC).
- The HRC binds to HRE (hormone-responsive element) and stimulates a specific gene. and the outcome is the production of a specific protein in response to hormone action.
HRE – A specific region on the DNA.
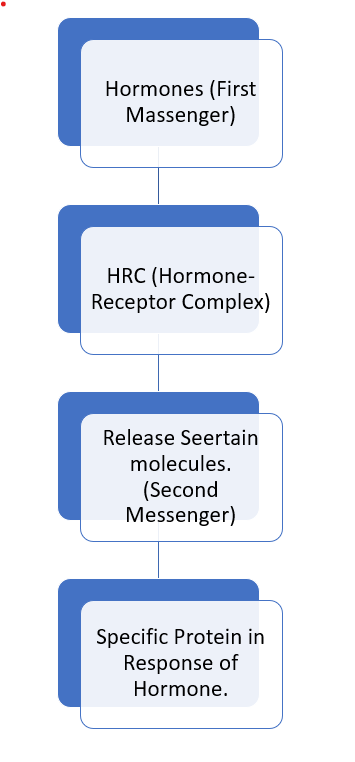
b. Group – II hormones
These hormones are lipophobic or hydrophilic. Most often they are protein hormones. Act through plasma membrane receptors and stimulate the release of certain molecules called second messengers. Hormones are the first messengers. The second messenger is –
(a) CAMP (Cyclic Adenosine 3 Monophosphate) eg. ACTH, FSH, LH, PTH, Glucagon, calcitonin.
(b) Phosphatidylinositol/calcium eg. TRH, GnRH, Gastrin, CCK.
(c) The second messenger is unknown eg. GH, Insulin, Oxytocin, and Prolactin.
Read Also-
Endocrine Quiz For Upcoming Nursing Exams
Online Nursing Test For AIIMS Rishikesh Exam
What is Vitamin A – Sources, Function & Deficiency