The mouth is the first part of the digestive system, also known as the oral cavity and buccal cavity. The mouth starts from the lips and ends at the throat. The structure of mouth / oral cavity includes the teeth, tongue, and salivary glands. The vestibule is the part of the mouth between the gums and the cheeks. And the part inside its gums is called the oral cavity.
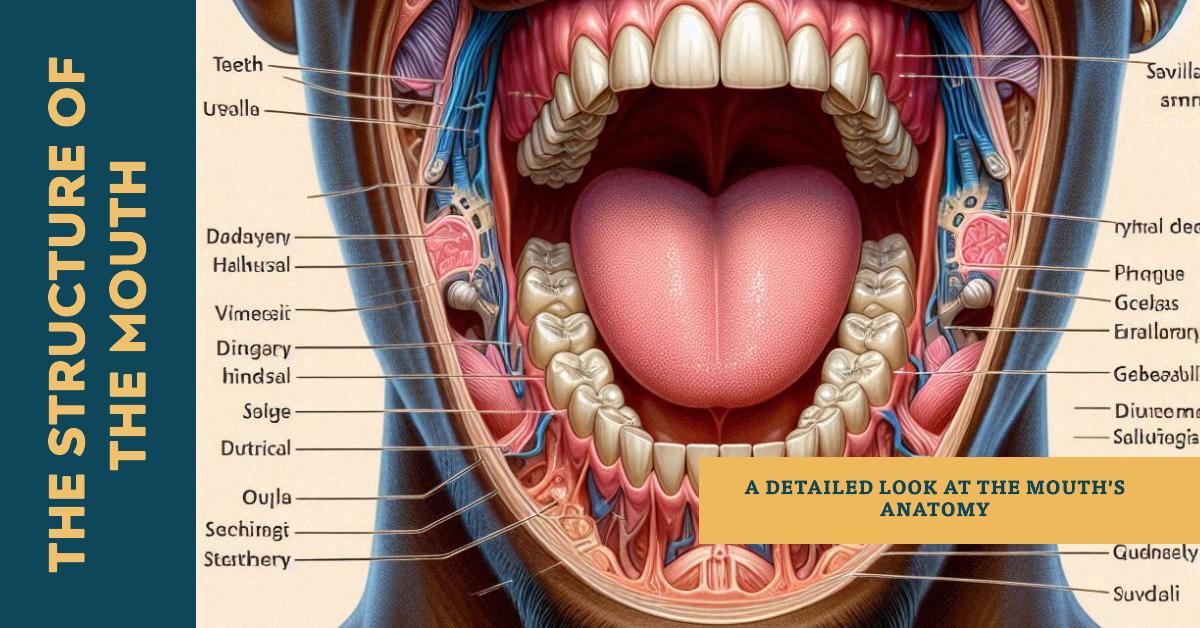
The roof of the mouth or the oral cavity is formed by the anterior hard and posterior soft palate. The hard palate is formed by two bones, the maxilla, and the palatine. The soft palate is fleshy and curves downward from the posterior end of the hard palate. And on the edges, it attaches to the walls of the pharynx. The uvula is a curved fold of muscle that is covered by a mucous membrane. which hangs between the free border of the soft palate. On either side of the uvula is a collection of lymphoid tissue called the palatine tonsils. The oropharynx starts on the backside of it, which is called the throat.
Structure of mouth-
The mouth or oral cavity is bounded by muscles and bones:
Anteriorly – by the lips
Posteriorly – it is continuous with the oropharynx
Laterally – by the muscles of the cheeks
Superiorly – by the bony hard palate and muscular soft palate
Inferiorly – by the muscular tongue and the soft tissues of the floor of the mouth.
Brief description of accessory organs in the structure of the mouth
- Lips– lips are two soft, movable, and muscular structures that form the opening of the mouth for the intake of food. Lips are used in eating, holding food, drinking inside, and also use in speaking. lips are tactile organs.
- The vestibule – It is a space between the soft tissue(lips and cheeks), and the teeth and gums. The vestibule is kept moist by secretion from the parotid salivary glands, which are located behind the angles of the jaw and in front of the ear.
- Mouth cavity – The mouth cavity lies posteriorly to the vestibule, bordered by several structures (roof, floor, and cheeks). the roof of the mouth cavity consists of hard and soft palates. and the floor of the mouth cavity consists muscular diaphragm, geniohyoid muscles, tongue, and salivary glands and ducts. mouth cavity kept moisture by the secretion of sublingual salivary glands and submaxillary salivary glands.
- Gums – gums are the tissue(fibrous and dance) of the upper jaw and lower jaw that surrounds the base of teeth. Gums are also known as gingiva.
- Teeth – The teeth are the hardest substances in our body. a person has one set of 20 primary teeth(baby or milk teeth)by the age of 3 years and replaced by permanent teeth(adult or secondary)human has 32 permanent teeth.
- Palate – Soft and hard palate forms the roof of the mouth, palate separates the mouth from the nasal cavity.
- Salivary glands – Three pairs of salivary glands produce saliva parotid glands, sublingual glands, and submandibular glands (submaxillary glands).
- The tongue – It’s a muscular organ made up of voluntary muscles. It is attached to the floor of the mouth by a fold of covering of a mucous membrane called the frenulum which is attached to the hyoid bone at its base.
- Uvula – Uvula is a hanging tissue that is located at the back of the throat in the soft palate.
The function of mouth-
Digestion starts in our mouth when we chew, food breaks down in tiny particles by teeth, and the salivary glands produce saliva. Saliva is a digestive juice in which moist food
and moist food moves easily through the esophagus into the stomach. saliva also has an enzyme that starts to break down the starch in our food.
Diseases of mouth-
- Cold sores
- Canker sores
- Thrush
- Leukoplakia
- Dry mouth
Read More-
Body Cavity – Definition and Structure
The Human Digestive System its parts and functions
STOMATITIS- Causes, Types & Signs/Symptoms
Structure of mouth, anatomical structure of mouth, human mouth structure, internal structure of mouth, oral cavity structure, anatomical structure of mouth and oral cavity