Definition – Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mucous lining of the mouth, which may involve the cheeks, gums, tongue, lips, and roof or floor of the mouth. This literally means inflammation of the mouth. It is a type of mucositis, a condition defined as pain or inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Introduction
- Inflammation of the soft tissue lining of any of the oral cavity
- Poor oral hygiene
- Dentures
- Mouth Burn from hot food or drinks
- Systemic conditions that affect the whole body as allergy, infection, or medications
Causes of stomatitis
- Chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
- Loose-fitting dental prosthetics
- Trauma
- Poor dental hygiene
- Smoking
- Hematologic malignancies (Its develop 2 to 3 times the rear of solid tumor)
- Infection viral fungal and bacterial
- Dehydration
- Medications
Asthma, types symptoms day and theme
Sign and symptoms of stomatitis
canker sores and cold sores
Canker sores
- Can be painful
- Its usually last 5 to 10 days
- Tends to come back
- Generally not associated with fever
Cold sores
- Are usually painful
- Usually gone in 7 to 10 days
- Associated with cold or flu like symptoms
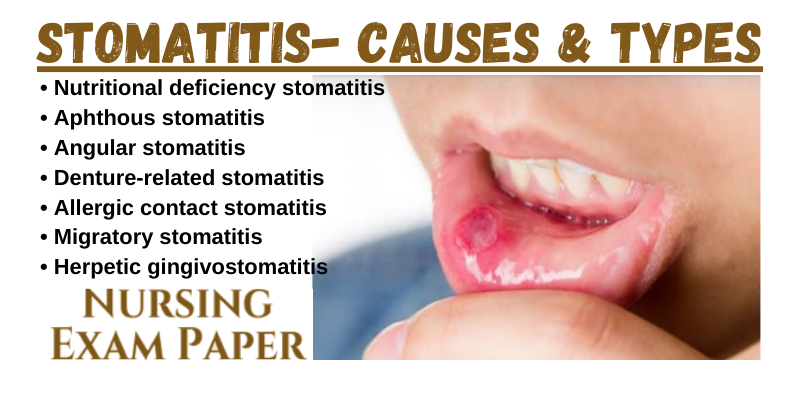
Types of stomatitis
- Nutritional deficiency stomatitis – Malnutrition or malabsorption can lead to nutritional deficiency status, for example, deficiency of iron vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, vitamin B9, vitamin B12 may all manifest as stomatitis. iron is necessary for the up-gradation or transcriptional elements for call replication and repair.
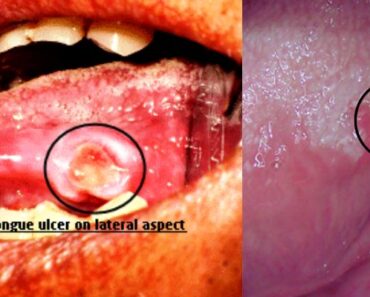
- Aphthous stomatitis – It is a disorder of unknown etiology that may cause significant morbidity. This is a common condition characterized by the repeated formation of a benign and non-contagious mouth ulcer in otherwise healthy individuals one or several discrete, shallow, painful ulcers are visible on the unattached oral mucous membrane.
- Angular stomatitis – Inflammation of the corners of the lips is Termed angular stomatitis or angular cheilitis.
- Denture-related stomatitis – It appears as Reddened but painless mucosa beneath the denture 90% of cases are associated with candida sepsis, and it is the most common form of oral Candidiasis.
- Allergic contact stomatitis – It is a hypersensitivity reaction that occurs in susceptible atopic individuals when allergic penetrate the skin, mucosa. Allergic content stomatitis appears as non-specific inflammation, so it may be mistaken for chronic physical irritation. There may be burning or soreness of the mouth and ulceration. chronic exposure to the allergen may result in a lichenoid lesion.
- Migratory stomatitis – Migratory is an atypical presentation of a condition which normally present on the tongue, Termed geographical tongue. Geographic tongue is so named because there are atrophic, erythematous areas of depopulation that migrate over time.
- Herpetic gingivostomatitis – This is inflammation of the mouth caused by the herpes simplex virus.
Treatment of stomatitis
ONLINE TEST SERIES FOR AIIMS RISHIKESH EXAM
The symptomatic treatment given in this includes
- Antiseptic mouthwash
- Protective pastes
- Local anesthetic mouthwash or spray
- Oral analgesics
- Topical corticosteroids
Nursing management
- The nurse instructs the present in the importance and techniques of Preventive mouth care.
- The nurse monitors the patient’s physical and psychological response to treatment.
- Advise the patient to avoid dry, bulky, and irritating foods and fluids, as well as alcohol or tobacco.
- Encourage the patient to increase fluid intake.